What is technical SEO and how is it done?
Technical SEO means optimising the technical backend of the website so that search engines can crawl, index and rank it effectively.
Unlike traditional SEO strategies, which involve creating quality and relevant content, technical SEO focuses on the behind-the-scenes factors that you cannot see directly. These issues impact how well search engines can find, index, and rank your website according to Neilpatel.
All technical aspects account for the overall health of the website, but a few of the most common ones are website speed, URLs and error handling. All of which and more we will discover in this article.
Why is Technical SEO important?
The technical SEO is the backbone of your website’s success. It allows search engines access and understand what your content is about and elevate that content in their search results.
When a site’s technical part is poorly optimized, it results in lower visibility and positions. Sometimes, it can even happen that the site is not ranking at all due to your settings and search engines can not access it.
In contrast, when we look at a website where the technical part is top-notch, it allows websites to maximize the efforts of SEO and traffic generation.
In short, it makes or breaks websites.
Why is technical SEO hard?
Technical SEO is complicated because it focuses on the infrastructure and technical aspects of websites that allow search engines to interact with your website.
Understanding, addressing, and fixing these key essentials is not always easy or straightforward. You really need to understand everything about websites: website development and design, SEO, coding, and so on.
To make things worse, each website is completely different. There are thousands of different themes and over 59,744 free plugins on WordPress alone (many of these also have paid versions).
That means each site will have different issues, some more complex than others. Understanding everything about all is impossible.
Thinking out of the box, searching for answers from the Internet, and testing and debugging becomes inevitable – and it takes lots of time.
What are the Factors that affect technical SEO?

8 common technical SEO factor’s we will discuss in this article are:
- Website speed
- Sitemap
- Robots.txt
- SEO-Friendly URLs
- Redirections
- Site architecture
- Internal links
- Technical errors
This is not by far limited list. Above mentioned factors are just one of the most common issue we have came across.
1. Website Speed and Performance
Website speed is not only crucial for your visitor’s load time but is also a ranking factor. Therefore, you need to make sure your site loads fast, ideally between 0-2 seconds. Anything slower is not sustainable for growth.
First, analyze with your computer browser and phone to see if it loads quickly or slowly. The best thing is to use incognito on Chrome or private on Safari, as this nulles your saved setting. Is it fast or not?
Now, use the search console if you have it set up (if you don’t, you should do so now). Navigate to Core Web Vitals under the experience tab and check if it shows that you pass performance for mobile and desktop.
If you have too little traffic or a new site, it may not show results there. So, alternatively, you can use Google PageSpeed Insights. It’s a tool provided by Google that allows you to analyze your website performance with suggestions on what to fix.
Other Tools for Measuring and Analyzing Speed:
Shortcut to increase website speed
There are 3 things that each website can do to increase around 80% of the speed, and these are:
- 1. Image compression
- 2. Cache setup
- 3. CDN
Image compression
Large image files are the number one factor slowing down a website. This is why image compression allows you to compress images without reducing their quality – at least, the human eye won’t recognize it.
Example:
- Original JPG image size: 2 MB
- Compressed JPG image size: 500 KB (75% smaller)
- JPG to WEBP converting size: 200 KB (90% smaller)
You can further compress it with Avif, but usually, it costs or requires an advanced setup.
Even if your site is on a website builder like Wix or Shopify, they compress your site images, but we have seen that manually compressing them beforehand gives a lot better results.
Cache setup
Cache means storing your website’s content on cache files. When visitors come to your site, their browsers request the file without having to download all the elements each time, resulting in much faster load times.
You can implement an effective cache through the WP Rocket plugin, which costs around €50 per year.
WP Rocket allows you to:
- Page Caching
- Browser Caching
- GZIP Compression
- Minify and combine CSS and JavaScript files
- Lazy Loading images
- DNS Prefetching
- Heartbeat Control
- Defer JavaScript Loading
- Preloading of fonts
- Database cleaning & optimization
In the end WP Rocket makes you a lot more money back in the long term than it costs.
Content Delivery Network (CDN) Implementation
A content delivery network (CDN) means storing your website’s static assets like images, scripts, and stylesheets on servers. When visitors access your site, the server closest to them provides these assets, reducing latency and improving page load time significantly.
For example, imagine you have a site in Finland. If someone from the US comes to your site, there is latency in how fast information gets there. Instead, you can have your assets saved on US servers, so they can retrieve the content much faster.
Tip: there is one free CDN by Cloudflare that each website can use.
2. Creating and Submitting Sitemaps
Sitemap is a page or file that includes links to all of your website’s pages, categories, and posts. It lays down the site architecture and makes search engines access and index your content faster.
Luckily, nowadays, we can use Rankmath or Yoast to implement XML sitemap.
Here are the steps to create an XML sitemap using Rank Math and then submit it to Google Search Console:
- Step 1: Install and Activate Rank Math
- Step 2: Configure Rank Math Settings
- Step 3: Enable XML Sitemap in Rank Math
- Step 4: Locate Your XML Sitemap URL
- Step 5: Submit XML Sitemap to Google Search Console
To locate the sitemap go to “Rank Math” > “Sitemap Settings.” You’ll find your XML sitemap URL at the top of the page.
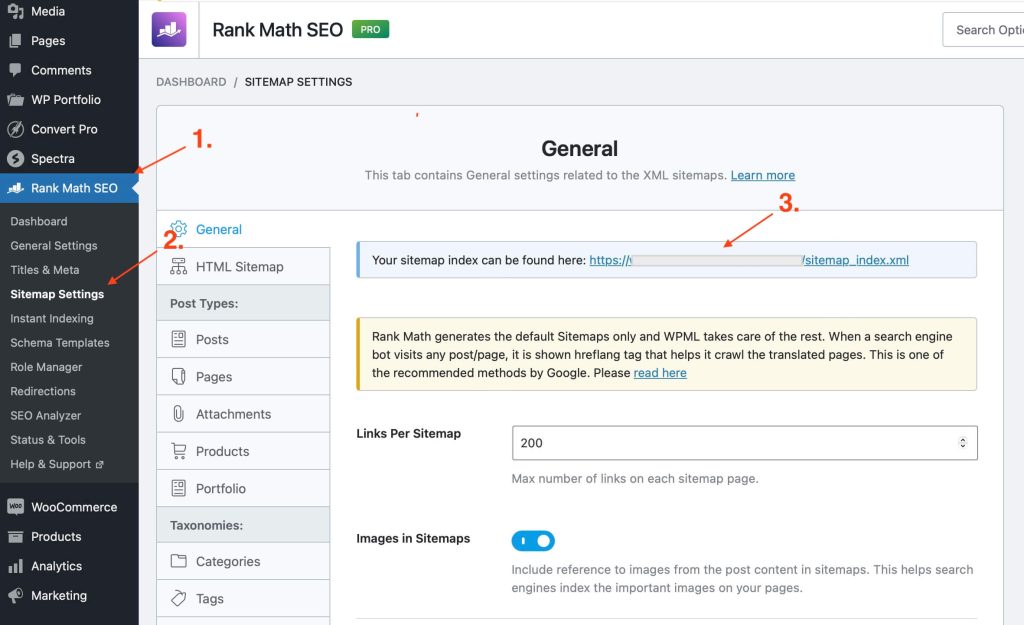
Or you can typically find it by adding /sitemap_index.xml to the end of your domain url, like: https://yourdomain.com/sitemap_index.xml.
Sitemap Best Practices
- Include only essential and indexable pages in the sitemap.
- Regularly update the last modification date for accurate indexing.
- Follow the XML sitemap protocol for proper syntax and structure.
3. Robots.txt File
The robots.txt files let search engine bots know which pages of your site should not be crawled.
Its especially useful if you have a large site and some bots try to mine data that hurts your server performance. All that is needed to do is to disallow that bot.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Disallowing Essential Pages: Avoid blocking search engines from crawling important pages unintentionally.
- Incorrect Syntax: Ensure proper syntax to prevent misinterpretation by search engine bots.
4. SEO-Friendly URL Structure
Example of Dynamic URL:
https://www.example.com/products?id=123&category=computer
Improved Dynamic URL:
https://www.example.com/products/computer/123
In the improved example, parameters are in a more structured way. That makes it easier for users and search engines to understand what information is on the page.
The exact same goes with any other page, post, category, or tag URLs – make them SEO-friendly.
But there is one crucial thing before you can do that. If you change the URLs of any content on your site, you need to make redirections from the old to the new URL. Read the next section to understand it.
5. URL Redirects
URL redirects are done when you remove or move a page that currently ranks for keywords and generates traffic, and you want to keep that SEO equity. All you have to do is take the old URL and redirect it to the new URL.
It is especially important when restructuring your website or making URLs SEO-friendly without losing the benefit of SEO.
Two of the main redirection you need to know are:
- 301 Redirect: Permanent Redirect
- 302 Redirect: Temporary Redirect
Let’s take one real life example of redirection
Let’s say you have a page that URL you want to make SEO-friendly.
For example, a Technical SEO page with the following URL:
https://www.example.com/what-is-technical-seo-and-how-its-done-and-how-much-does-it-cost
You change the URL to:
https://www.example.com/what-is-technical-seo
You need redirect the old link:
Redirect 301 /https://www.example.com/what-is-technical-seo-and-how-its-done-and-how-much-does-it-cost https://www.example.com/what-is-technical-seo
The same goes with every other page, product, and category.
But the next thing becomes very important here…
Avoid redirct chains
Redirect chain happens where you chain multiple redirects together.
For example, you redirect from page A to page B. Then you make a new redirect from page B to page C.
Why it’s bad?
The reason is that search engine crawlers must go through each link to find your end content, and your visitor’s browser must request 3 HTTP requests.
Not only does it slow down your site server through additional requests, but it also leads to unnecessary delays in page loading for visitors. With each chain, it increases, making it worse and worse.
By fixing redirect chains, you reduce the number of HTTP requests and improve page speed. Better yet, avoid them in the first place.
6. Site Architecture
It means structuring your website’s content in a logical and structured manner to make its relationship easy to understand.
Example of simple and logical website architecture:
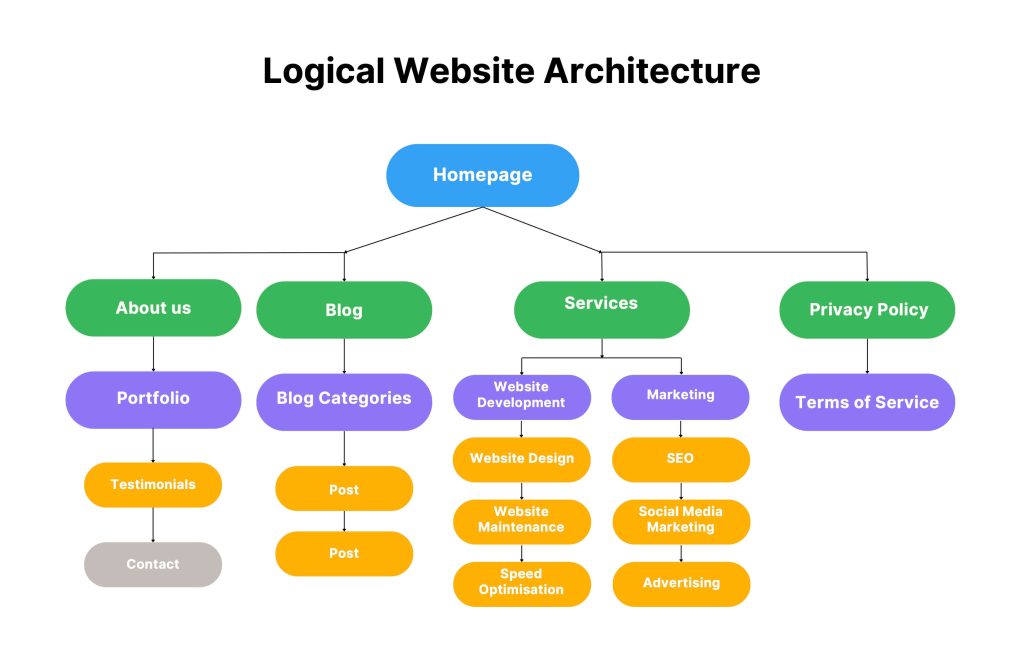
In this example, The Homepage serves as the root, and main categories like About us, Blog, Services and Privacy Policy branch out into subcategories, creating a clearly unreadable site hierarchy.
7. Internal Linking Strategies
Internal links mean linking from one page to another. Not only does it improve your navigation, but also distributes the SEO authority effectively around your content (also referred to as link juice).
The main goal of the internal link strategy is to build a cluster. This means linking relevant content with each other.
For example, have a link from the homepage to all services. From each main service page or categories, you want to have a link to subcategories and/or products. From each subcategory, you should have one link back to the main category, either through the normal link and anchor text or breadcrumb. And at least one link to the following relevant subcategory. This way SEO link juice flows around your related content, helping it rank better.
8. Technical Errors
Technical SEO errors occur over time as you make changes to the site and content, but do not understand what happens at the back end. These errors negatively impact your site’s SEO performance and user experience. Identifying and fixing them becomes a key of maintaining a healthy website.
Common errors that you may come across are, but are not limited to:
- Crawling errors
- Links to 404
- Thin or duplicate content
- Missing or duplicate h1 heading
- Meta description missing or too short
- Pages speed issue
- Structured data problems
- And many others.
How can you find technical errors?
Sign up for free webmaster tools by Ahrefs. It is a paid SEO analysis and research tool, but they offer this amazing free tool to monitor your website’s technical issues.
Here’s how it works:
- 1. Sign up to Ahrefs Account
- 2. Add Your Website: You need to add your site and verify it using the search console, which is the fastest way.
- 3. Crawl Your Website: Navigate to the Ahrefs Site Audit tool and click crawl. With new sites, it can do it automatically. Just wait until it’s completed.
- 4. Review Site Health Score: Anything above 80-90 is usually good, but not always.
- 5. Identify Errors: Navigate through errors to see what they are and learn how to fix each.
- 6. Fix Technical SEO Issues: All that’s left is to find a way to fix each. Some issues are as easy as adding content. Others can be more technical.
After you run your audit you should see something like that:
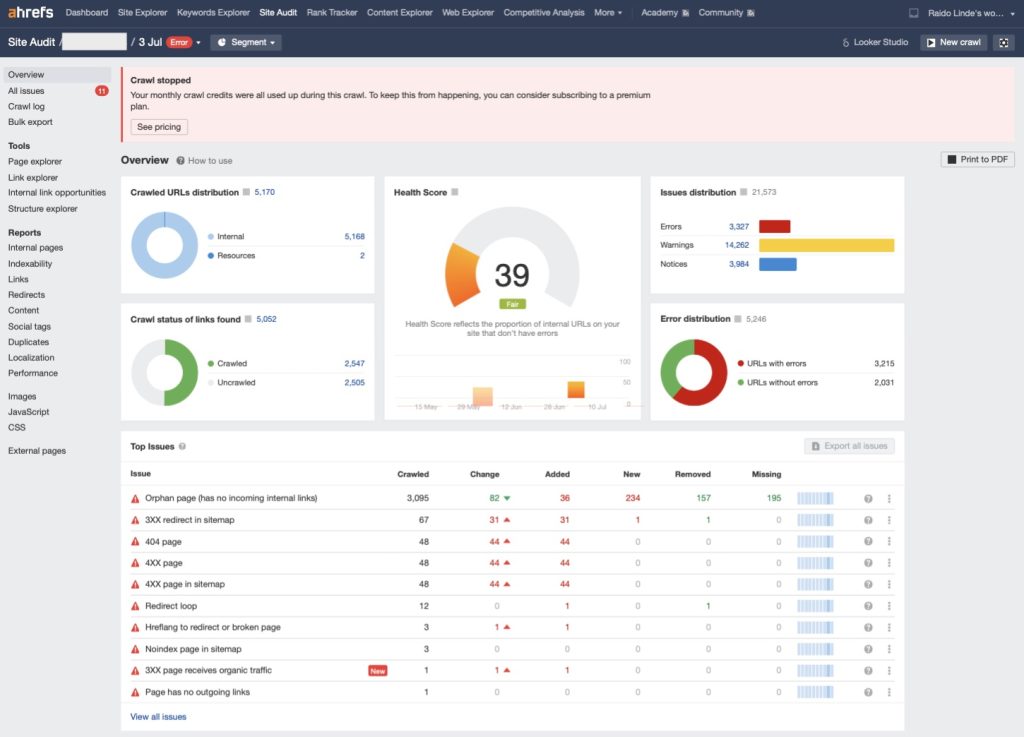
Anything below 80 usually needs fixing.
If you click any SEO “Top issues” in the dashboard, each will open up with the list of problems. All you need to do is fix them or hire someone.
Most monthly SEO packages start by analyzing and fixing your technical SEO issues, which is why it’s best to go for a monthly retainer.
After you fix most errors, the score should be above 80:
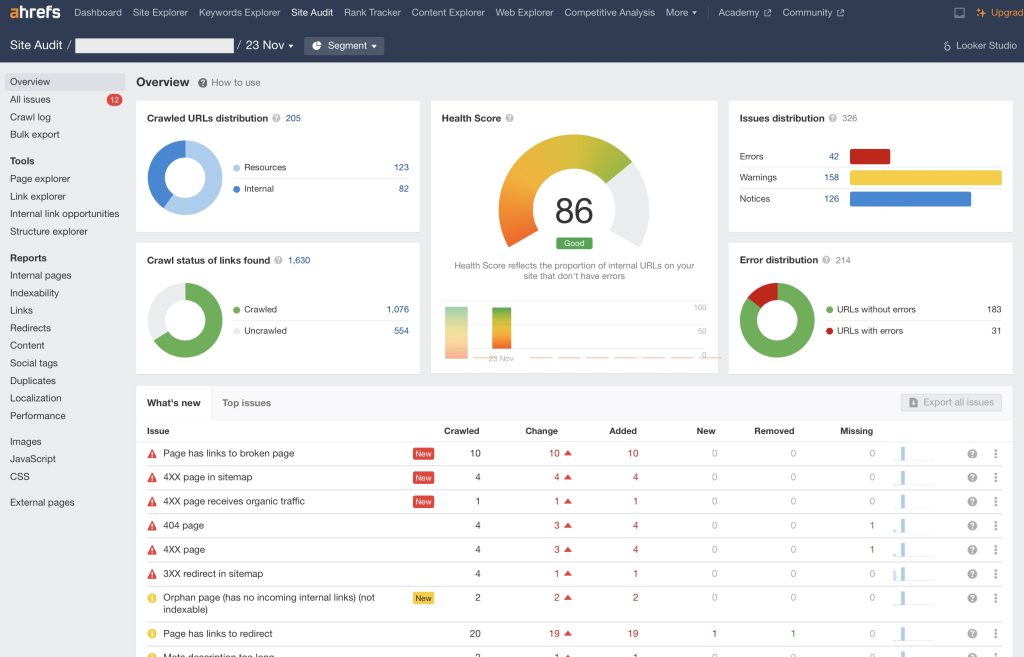
Anything between 80-100 score is usually good, and some errors you can’t or do not even need to fix. But do not take it for granted. There could be still something hindering your website’s performance. So, check everything regardless of what score you receive.
NB! There is a certain amount of crawl budget (I guess 10000 links) per month that Ahrefs allows for free, so be careful not to use it all in one go. Especially if you have a large site or have many no-follow pages that you wish not to analyse. You should first stop the initial crawling and remove unwanted things from future crawls. Then initiate the audit again.
Remember: If you do not have time yourself or lack the skills, you can always contact us, and we can help.
Get a free SEO quote now!
Let our SEO experts audit your website and put together custom plan and quote for your business.
Additional SEO resources
Here is a list of SEO blogs and resources for you to consider
What is SEO?
Search engine optimisation means means making your websites content available for search engine crawlers, so that it can be indexed and ranked in search results. Learn more about it.
SEO prices
Learn the most important factors of a backend of your website that makes or breaks your SEO success.
SEO training
Learn how to perform SEO on your own with 7 days free training. Each days training is sent straight to your email.
